Why is there only 21 million bitcoin
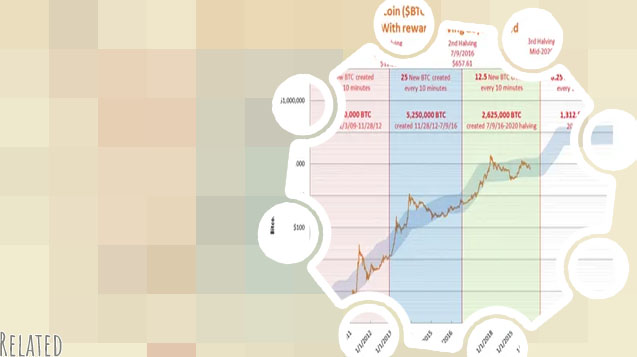
Bitcoin's scarcity is a well-known feature that sets it apart from traditional fiat currencies. With only 21 million bitcoins ever to be mined, this digital asset has garnered much attention and speculation. To better understand the implications of this finite supply, we have curated a list of two articles that dive deeper into the topic of 21 million bitcoins.
The Significance of Bitcoin's 21 Million Supply Cap

Bitcoin's 21 million supply cap is a key feature that sets it apart from traditional fiat currencies and other cryptocurrencies. This limit on the total number of bitcoins that can ever be created plays a crucial role in maintaining the digital currency's scarcity and value. Here are some reasons why this supply cap is significant:
-
Scarcity: With a fixed supply of 21 million bitcoins, the digital currency is inherently scarce. This scarcity is similar to precious metals like gold, which have limited supplies that cannot be artificially inflated.
-
Store of Value: The limited supply of bitcoins makes it an attractive store of value for investors looking to hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. As the demand for bitcoin grows, its scarcity can help drive up its price over time.
-
Decentralization: The 21 million supply cap is a key factor in bitcoin's decentralized nature. Unlike fiat currencies that can be printed at will by central banks, the fixed supply of bitcoins ensures that no single entity can control the currency's issuance.
-
Economic Consistency: The predetermined issuance schedule of bitcoins, which halves approximately every four years through a process known as "halving," helps to maintain economic consistency within the bitcoin network. This predictable supply growth can help prevent sudden inflation or deflation.
Exploring the Economics Behind Bitcoin's Fixed Supply Limit
Bitcoin's fixed supply limit plays a crucial role in understanding the economics behind this popular cryptocurrency. With only 21 million Bitcoins ever to be mined, scarcity is built into the system, which in turn affects its value and price dynamics. This unique feature sets Bitcoin apart from traditional fiat currencies, where central banks can print more money at will, leading to inflation.
Here are some key points to consider when exploring the economics behind Bitcoin's fixed supply limit:
-
Scarcity and Demand: The limited supply of Bitcoin means that as demand increases, its value is likely to rise. This is in stark contrast to fiat currencies, where the supply can be inflated, leading to a decrease in purchasing power over time.
-
Mining and Halving: The process of mining new Bitcoins becomes increasingly difficult over time, leading to a gradual decrease in the rate of new coin creation. Additionally, the halving event, which occurs approximately every four years, reduces the reward for miners by half, further limiting the supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation.
-
Store of Value: Many proponents of Bitcoin argue that its fixed supply makes it an ideal store of value, similar to gold. The scarcity of Bitcoin makes it resistant to inflation, making it an attractive asset for investors looking to hedge against economic uncertainty.